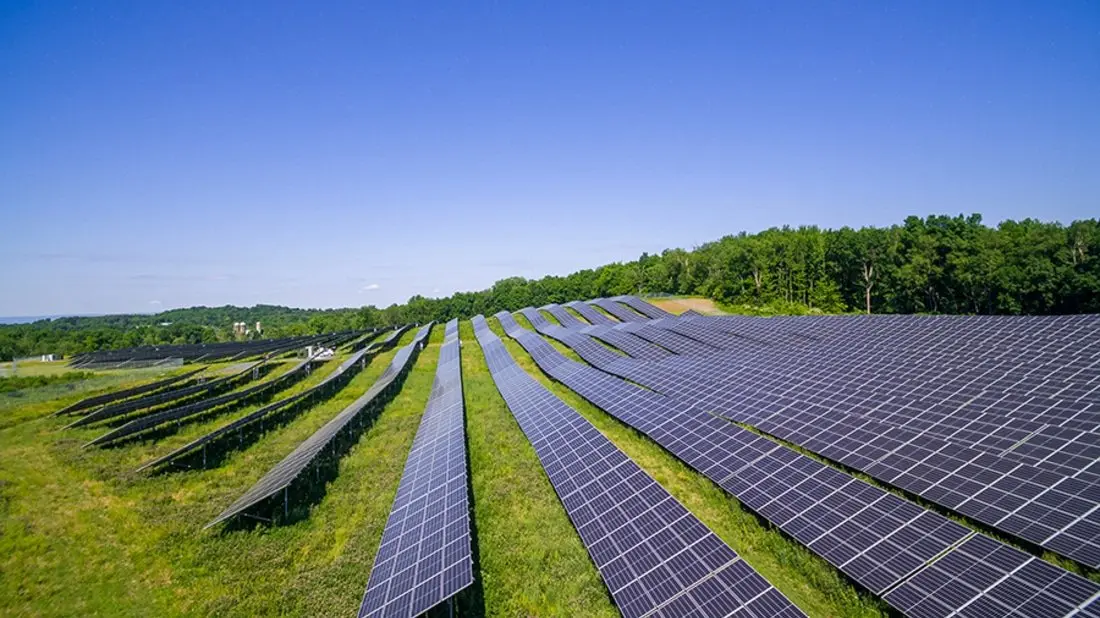
Solar energy has become a popular way to generate electricity for many homeowners. It is a great way to help the environment and save money.
It is no secret that fossil fuels are dirty and bad for the environment. But what is not commonly known is that there are solutions.
Cost
The average cost of solar panels and systems has fallen in the last decade. This, along with the energy cost savings a system provides, has made home solar one of the most competitive ways consumers can green their electricity consumption and reduce their utility bills.
As a result, the number of homeowners installing renewables has spiked. But for many, the high up-front investment in a solar photovoltaic (PV) system is prohibitive. The good news is that the financial hurdle has been significantly lowered based on the latest federal tax incentives.
In Odessa, Texas, workers at a solar-recycling company unload trucks loaded with end-of-life PV panels from across the country. They separate the glass from the aluminum frames and grind and shred the laminated materials into a patented process that sifts out the valuable silver and copper. This is the first step in a journey that could turn the massive volume of retired solar modules into raw materials used to make new, high-efficiency solar cells and systems.
The global supply chain needs to quickly build capacity that will allow the recapture and reuse of the estimated 78 million PV modules expected to retire by 2050. This includes a broader circular economy that enables the safe transport and storage of the modules until they are ready to be recycled.
Energy Independence
Despite high upfront costs, homeowners and businesses who install solar energy systems can see financial savings over time. They also become their energy providers, reducing reliance on the electrical grid and helping to protect themselves from volatile fossil fuel prices and outages caused by extreme weather.
Solar energy is also environmentally friendly, reducing reliance on finite natural resources such as coal and oil. Additionally, it does not produce greenhouse gases or other air pollutants that contribute to climate change. However, it is essential to note that solar panels only work when the sun is shining and that energy generated from them must be stored at night or during cloudy weather.
Fortunately, researchers are working to address these issues as technology advances. Some of the most promising technologies include photovoltaic cells with different materials that can draw energy from both parts of the spectrum and battery-based storage systems.
These advancements are expected to drive solar energy adoption further as it becomes more affordable and increasingly accessible. The solar industry is expanding so quickly that middle-income households now make up a significant percentage of new customers, as opposed to only higher-income households that went solar in the past. It is clear that America has the potential to become a leading solar powerhouse, but it will require strong policy leadership and innovation to do so.
Sustainability
Solar energy is a renewable resource that will never run out, unlike fossil fuels which are finite and release harmful greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere when burned. This makes solar power a much more sustainable energy source that reduces dependence on the earth’s dwindling natural resources and conserves water.
The most obvious benefit of a residential solar energy system is the savings on electricity costs. However, there are other environmental benefits to consider too. By generating your electricity through a home solar panel system, you’ll become less reliant on the grid and are less impacted by any potential disruptions in power. Many homeowners pair their solar panels with battery storage, known as solar-plus-storage systems, to increase their energy supply’s reliability.
Another critical point is that solar panels are fully recyclable, made from glass, metal, and silicon. However, at present, we need more infrastructure to facilitate this recycling on a large scale. As the first wave of early-replacement solar systems reaches their end-of-life, legislation will likely be enacted to encourage panel recycling or make the process easier.
This is a positive step forward, but more needs to be done. If legislation is enacted later, we will find ourselves with a growing pile of waste and limited options to deal with it.
Job Creation
As solar technology expands, so does the demand for workers to produce and install it. This is a massive boon for the economy, creating jobs across numerous industries. It’s also a great way to help the environment by reducing emissions.
Solar energy is becoming more popular as people become more concerned about the environment and want to use sustainable power sources. However, it is only for some. The high upfront cost of solar panels makes it a challenging investment for many families to afford, especially those who live in cloudy areas. Luckily, the solar industry is working to improve the financial viability of solar systems by lowering costs and improving efficiency.
As the renewable energy sector continues to grow, it’s essential to understand how each state is performing in terms of jobs in renewables. The map below shows one way to do this by comparing job creation in the sector with each state’s natural potential for wind and solar power. Each dot represents a different state, with some doing very well in the sector and others lagging. This chart is based on data from the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA). Click on each state to see more detailed information. The states with the most jobs in solar are California, North Carolina, and Texas. These three states also have the highest natural potential for solar and wind power.