Introduction to Form 5471
Navigating the complexities of international tax reporting can feel like diving into a maze without a map. One crucial form that individuals with foreign investments or ownership in foreign corporations must grapple with is Form 5471. Understanding this form is essential to stay compliant and avoid hefty penalties. Let’s unravel the intricacies of Form 5471 together, demystifying its requirements and shedding light on why getting it right matters.
Who is Required to File Form 5471?
If you have ownership in a foreign corporation, Form 5471 may be on your radar. So, who exactly is required to file this form? Well, if you’re a U.S. person who meets certain ownership thresholds or has control over a foreign corporation, then Form 5471 is likely in your future. Individuals holding at least 10% ownership in a foreign corporation during the tax year are typically obligated to file. Additionally, officers or directors of foreign corporations with U.S. shareholders may fall under the filing requirements as well.
It’s essential to understand that even if you don’t receive income from the foreign corporation, you might still need to report it on Form 5471. The IRS keeps a close eye on international transactions and holdings for transparency and compliance purposes.
Navigating the rules around who needs to file Form 5471 can be complex but understanding your obligations upfront can save you headaches down the road.
Different Categories of Filers
When it comes to Form 5471, there are different categories of filers based on their involvement in foreign corporations. The first category includes US citizens or residents who own at least 10% of a foreign corporation’s stock value.
Another category comprises individuals who control a foreign corporation for at least 30 days during the year, known as Category 2 filers. These individuals must report detailed financial information about the company.
Category 3 filers are US shareholders in controlled foreign corporations with specific transactions or investments triggering reporting requirements. They need to disclose details like income, balance sheet items, and more.
Category 4 covers certain US persons who are officers or directors of a foreign corporation where other categories don’t apply. Understanding these categories is crucial for accurate filing and compliance with international tax laws.
Information Required on Form 5471
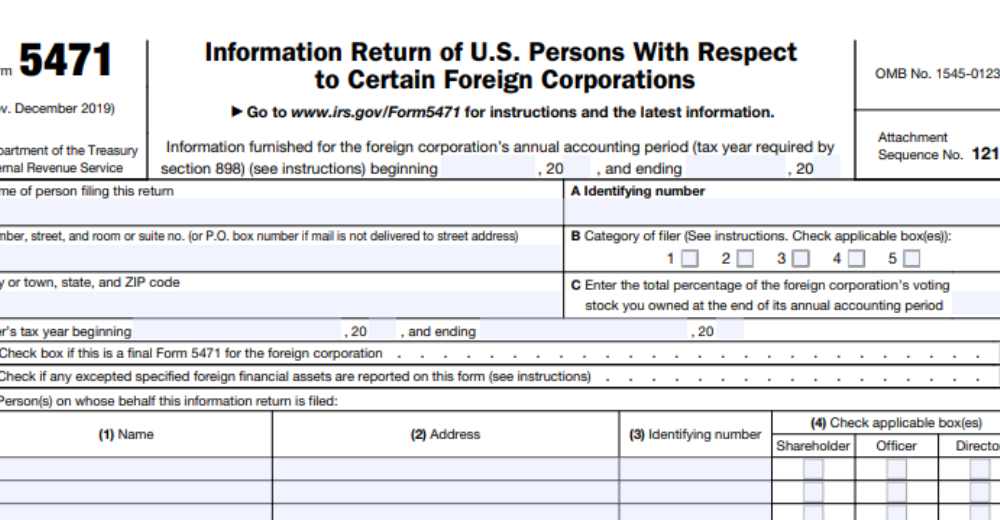
Form 5471 is a detailed form that requires extensive information about foreign corporations and their shareholders. When completing this form, you will need to provide details such as the name and address of the foreign corporation, its business activities, financial statements, and ownership structure. Additionally, you must disclose any transactions between the foreign corporation and related parties.
Furthermore, Form 5471 requires information on the U.S. shareholders of the foreign corporation, including their names, addresses, tax identification numbers, and percentage of ownership. It’s crucial to accurately report all required information to ensure compliance with international tax regulations.
In addition to basic information, Form 5471 may also require specific schedules depending on your relationship with the foreign corporation. These schedules provide further insight into the nature of your involvement with the entity and help tax authorities assess potential risks for tax evasion or avoidance.
Understanding what information is needed on Form 5471 is essential for accurate reporting and avoiding penalties for non-compliance.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
When it comes to Form 5471, non-compliance can have serious consequences. Failing to file this form or inaccurately reporting information can result in hefty penalties. The IRS takes international tax reporting seriously, and not meeting the requirements can lead to financial repercussions.
Penalties for non-compliance with Form 5471 may include substantial fines that could add up quickly. Additionally, there might be potential legal implications if the IRS determines willful neglect or intentional disregard of the filing requirements.
It’s crucial for individuals and businesses with foreign investments or interests to understand their obligations under Form 5471 and ensure they are accurately reported. Seeking professional advice from a tax expert specializing in international tax matters is advisable to avoid potential penalties and issues down the line.
Tips for Filing Form 5471 Correctly
When it comes to filing Form 5471 correctly, attention to detail is key. Start by familiarizing yourself with the form and its requirements. Ensure that you have all the necessary documentation and information ready before beginning the filing process.
Double-check your entries for accuracy and completeness to avoid any errors or omissions that could lead to penalties. It’s important to stay up-to-date on any changes in tax laws or reporting regulations that may impact your filing.
Consider seeking assistance from a tax professional with experience in international tax matters if you feel unsure about completing Form 5471 accurately. They can provide guidance and ensure that your submission meets all necessary requirements.
Don’t rush through the process – take your time to review everything thoroughly before submitting. By following these tips, you can increase your chances of successfully filing it without any issues.
Pros of Form 5471
It comes with its fair share of advantages for taxpayers navigating the complexities of international tax reporting. One significant benefit is that it provides a comprehensive overview of foreign assets and investments, helping to ensure compliance with IRS regulations. By filing it, individuals can avoid potential audit triggers and penalties associated with undisclosed foreign financial interests.
Moreover, this form allows for potential tax savings through various credits, deductions, or deferrals related to international business activities. It also helps in maintaining transparency with the IRS about offshore accounts and investments. Additionally, by accurately completing it, taxpayers can establish a clear record of their foreign holdings and transactions.
It serves as a valuable tool for individuals involved in overseas businesses or investments to stay compliant with US tax laws while maximizing tax benefits within the legal framework.
Cons of Form 5471
While Form 5471 is a vital tool for reporting international financial interests, there are some cons to consider. One of the main drawbacks is the complexity and detailed nature of the form itself. It requires a thorough understanding of tax laws and regulations, which can be overwhelming for individuals not well-versed in this area.
Another downside is the potential for significant penalties if the form is not filed correctly or on time. The IRS takes non-compliance seriously and imposes harsh fines for errors or omissions on it. This adds pressure and stress to taxpayers who must ensure accuracy in their filings.
Moreover, gathering all the necessary information to complete Form 5471 can be time-consuming and tedious. The extensive documentation required may require assistance from professionals, leading to additional costs for taxpayers seeking compliance with international tax reporting requirements.
While Form 5471 serves an essential purpose in providing transparency regarding foreign financial interests, its complexities and potential consequences make it a challenging aspect of international tax compliance.
Conclusion
As we wrap up this discussion on Form 5471, it’s important to reflect on the complexities and nuances involved in international tax reporting. Navigating the requirements of Form 5471 can be challenging for many individuals and entities with foreign investments or interests.
Understanding who needs to file, what information is required, and potential penalties for non-compliance are crucial aspects to consider when dealing with Form 5471. It’s essential to approach this form with attention to detail and accuracy to avoid any issues down the line.
While there are pros and cons associated with filing Form 5471, it ultimately serves as a vital tool in promoting transparency and compliance in cross-border transactions. By staying informed about international tax reporting obligations, individuals can ensure they remain compliant with IRS regulations.
Staying proactive in understanding Form 5471 requirements is key for those engaged in overseas business activities or investments. Remember that seeking professional advice can help navigate the complexities of international tax reporting effectively.
FAQs
Q: What is the deadline for filing Form 5471?
A: The deadline for filing Form 5471 is typically the same as your individual income tax return, including extensions.
Q: Is there a way to request an extension for filing Form 5471?
A: Yes, you can request an extension by filing Form 7004 on or before the regular due date of your return.
Q: Are there any exceptions to the requirement of filing Form 5471?
A: There are certain exceptions and specific rules that determine whether you need to file this form based on your involvement with foreign corporations.
Remember, when it comes to international tax reporting and compliance, it’s crucial to stay informed about the requirements and regulations. If you have any doubts or questions regarding Form 5471, consulting with a tax professional or accountant who specializes in international taxation can provide invaluable assistance. Stay proactive in understanding and meeting your obligations to avoid potential penalties and ensure smooth operations across borders.